Google’s June 2025 Core Update: What You Need to Know
The digital landscape is a dynamic realm, constantly reshaped by the subtle yet profound shifts in search engine algorithms. For content creators, businesses, and digital marketers, these shifts are not mere technicalities; they are seismic events that can redefine visibility, traffic, and ultimately, success. On June 30, 2025, Google once again sent ripples through this landscape with the official announcement and rollout of its June 2025 Core Update. This comprehensive adjustment to Google’s ranking systems, slated to take up to three weeks for a full rollout, is poised to reward genuinely helpful, high-quality content while putting renewed pressure on anything that falls short of Google’s evolving standards.
What is a Google Core Update? The Philosophy Behind the Recalibration
To understand the June 2025 update, it is essential to grasp the fundamental nature of Google’s core updates. These are not targeted penalties for specific transgressions, nor are they minor tweaks to the algorithm. Instead, Google views them as broad, systemic recalibrations designed to enhance its ability to deliver the most relevant, reliable, and satisfying content to searchers.
Imagine compiling a list of your favorite restaurants. Over time, new, exceptional establishments emerge, and existing ones might improve or decline. When you update your list, restaurants that move down aren’t necessarily “bad”; it simply means there are now better, more fitting options for your current preferences. Google applies a similar logic to its vast index of web pages. Core updates are about Google continually refining its understanding of what constitutes “great” content and how best to surface it amidst the ever-growing ocean of information online.
This philosophy underscores the core advice Google consistently offers: focus on creating excellent content for people, not just for search engines. The June 2025 update, like its predecessors, reinforces this principle, aiming to reward websites that genuinely serve user intent with high-quality, trustworthy, and people-first information.
The Key Pillars of the June 2025 Core Update: What’s Being Emphasized?
While Google rarely reveals the intricate specifics of its algorithm changes, industry observations and Google’s consistent guidance allow us to discern the likely focus areas of the June 2025 update. These include:
- Elevated Content Quality Evaluation: This remains the cornerstone. Google is increasingly sophisticated in identifying content that is truly in-depth, valuable, original, and well-researched. The update is expected to prioritize content that goes beyond superficial summaries or keyword-stuffed articles, favoring those that provide comprehensive answers and unique insights. Websites churning out thin, low-value, or excessively AI-generated content (especially without human oversight and refinement) are likely to face significant challenges.
- Reinforced E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): The E-E-A-T framework continues to be a critical signal. Content that clearly demonstrates the creator’s or organization’s genuine experience, deep expertise, established authoritativeness, and unwavering trustworthiness is more likely to thrive. This is particularly crucial for “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) topics like health, finance, and legal advice, where accuracy and credibility are paramount. Sites that showcase real-world experience, verifiable credentials, and transparent authorship are expected to see improved performance.
- Enhanced User Experience (UX) Signals: A website’s usability plays a significant role in its perceived quality. Factors such as fast page load times, intuitive navigation, mobile-friendliness, and overall site performance contribute to a positive user experience. The June 2025 update is likely to reinforce the importance of these technical and design elements. Sites that are slow, clunky, or difficult to use on mobile devices may find themselves disadvantaged.
- Combatting Low-Value and AI-Generated Content: While Google has stated it’s not inherently against AI-generated content, it is strongly opposed to content generated at scale purely for ranking purposes, lacking originality, value, or human insight. Early observations from the June 2025 update suggest increased pressure on such content, with reports of low-value, thin, or outdated pages being deindexed or losing significant visibility. This aligns with Google’s ongoing efforts to clean up search results and reduce spam.
- Visibility for User-Generated Content (UGC) Platforms: Interestingly, some initial observations suggest a potential increase in visibility for platforms heavily reliant on user-generated content, such as Reddit. This could indicate Google’s continuing exploration of how valuable, authentic discussions and experiences shared by real users can enrich search results, provided they meet quality thresholds.
The Rollout and Initial Impact: What to Expect
The June 2025 core update began rolling out on June 30, 2025, and is projected to take approximately three weeks to complete. This extended rollout period, compared to the typical two weeks of previous updates, means that website owners and SEOs should expect sustained volatility in rankings and traffic during this time.
Initial reports from early July indicate that some sites are already experiencing significant fluctuations, with both gains and losses observed across various industries. While some SEO tools are showing early signs of volatility, the full impact will only become clearer as the update progresses and fully propagates across Google’s data centers. It’s crucial to remember that fluctuations during a core update are normal, and a definitive assessment should only be made after the rollout has completely settled.
Navigating the Aftermath: A Strategic Approach to Recovery and Growth
For website owners and digital marketers, the June 2025 core update serves as a powerful reminder of the continuous need for adaptability and a user-centric approach. If your site experiences a decline in rankings or traffic, resist the urge to panic and implement immediate, reactive “fixes.” Instead, adopt a measured and strategic approach:
- Don’t Panic, Diagnose Holistically: Avoid knee-jerk reactions. Give the update time to fully roll out and for the search results to stabilize. Then, thoroughly analyze your data. Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to identify which pages or sections of your site have been most affected. Look for patterns in the decline – is it specific content types, topics, or site areas?
- Conduct a Comprehensive Content and Quality Audit: This is the most crucial step. Honestly assess your content against Google’s quality guidelines and the principles of E-E-A-T. Ask yourself:
- Does our content provide original information, in-depth reporting, or insightful analysis?
- Is it more substantial and valuable than competing content?
- Is it accurate, up-to-date, and free of grammatical errors or factual inaccuracies?
- Does it truly answer the user’s query and satisfy their intent?
- Is the authorship clear, and are the authors credible experts in their field?
- Does the content demonstrate genuine experience?
- Is there any low-value, thin, or auto-generated content that offers little to no unique value? Consider consolidating or improving such content, or even removing it if it cannot be salvaged.
- Enhance User Experience (UX): Review your website’s technical performance and usability.
- Are your Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, Cumulative Layout Shift) up to par?
- Is your site mobile-friendly and responsive across all devices?
- Is the navigation intuitive and easy to use?
- Are there excessive ads or intrusive pop-ups that detract from the user experience?
- Analyze Your Competition: Identify who has gained visibility in your target keywords. What are they doing differently? Can you glean insights into content depth, E-E-A-T signals, or user experience elements that might be contributing to their success?
- Focus on Meaningful, Sustainable Improvements: Core updates signal a need for broad, impactful changes, not minor tweaks. Prioritize significant content updates, improvements to your site’s overall authority, and enhancement of the user journey. For instance, consider adding detailed author bios, incorporating original research, expanding on existing topics with more depth, or improving internal linking to relevant, authoritative pages.
- Be Patient: Recovery from a core update is rarely instantaneous. Improvements you make now may not fully manifest until Google’s systems have re-evaluated your site, which can take weeks or even months, sometimes aligning with the next broad core update. SEO is a long-term investment, and consistency in delivering value will ultimately be rewarded.
The June 2025 core update, while a moment of volatility for many, is ultimately an affirmation of Google’s unwavering commitment to quality and user satisfaction. For those who prioritize creating truly helpful, reliable, and people-first content, this update represents not a threat, but an ongoing opportunity to strengthen their position in the evolving world of search. By understanding its underlying principles and responding with thoughtful, strategic improvements, website owners can weather the storm and emerge stronger in the digital currents.
Search Engine Optimization (seo) in Digital Marketing
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in ensuring online visibility, traffic, and growth for businesses. Whether you’re a blogger, a business owner, or a digital marketer, understanding SEO is vital for success.
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of improving a website’s visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The main goal of SEO is to increase organic (non-paid) traffic to a website by ensuring it appears higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant keywords.
SEO involves several key elements, including on-page SEO (optimizing content, HTML tags, and site structure), off-page SEO (building backlinks and social signals), and technical SEO (enhancing site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability).
Search engines use complex algorithms to determine which websites offer the most relevant and trustworthy content. SEO helps align your website with these algorithms by improving keyword usage, providing valuable content, and ensuring a positive user experience.
1. Introduction to SEO
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) refers to the process of optimizing your website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). It involves both on-page and off-page strategies that help search engines like Google understand, index, and recommend your content to users.
2. Importance of SEO in Digital Marketing
SEO is a core pillar of digital marketing. It brings organic traffic to your site without paying for ads. A well-optimized website:
- Increases visibility
- Builds credibility and trust
- Enhances user experience
- Drives more conversions
- Offers long-term ROI
Unlike paid advertising, SEO focuses on sustainable growth.
3. How Search Engines Work
Search engines like Google use web crawlers (bots) to discover content across the web. They crawl, index, and rank web pages based on hundreds of factors including relevance, quality, speed, and usability.
Per the Google SEO Guide, the goal of SEO is to improve how Google finds and displays your content.
4. Key SEO Practices Based on Google Guidelines
Here are some essential SEO practices directly aligned with Google’s official guidance:
a. Website Structure & Navigation
- Create a clear site hierarchy.
- Use breadcrumb menus and internal links to help users and bots navigate.
- Submit a sitemap.xml and use robots.txt effectively.
Google recommends creating a logical link structure where every page is reachable through at least one static text link.
b. Optimized Content Creation
- Write for users first, not search engines.
- Use keywords naturally in titles, headers (H1, H2), and content.
- Focus on original, informative, and engaging content.
c. Meta Tags and Descriptions
- Use relevant title tags and meta descriptions.
- Keep title tags under 60 characters and meta descriptions under 160 characters.
- Avoid duplicating meta information across pages.
d. Mobile-Friendliness
- Use responsive design to ensure usability across devices.
- Google primarily uses the mobile version of the site for indexing.
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test Tool to verify your site’s performance.
e. Image Optimization
- Use descriptive filenames and alt attributes.
- Compress images to improve loading speed.
- Implement lazy loading where appropriate.
f. Link Building & Internal Linking
- Create high-quality backlinks from authoritative sites.
- Use anchor text that’s descriptive and relevant.
- Maintain a healthy internal linking structure to connect related pages.
g. URL Structure & Canonicalization
- Use clean, readable URLs (e.g.,
/seo-tipsnot/page?id=42). - Implement canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues.
5. Technical SEO Tips
Technical SEO ensures that your website meets the technical requirements of modern search engines. Based on Google’s guide, pay attention to:
- HTTPS encryption: Secure your website.
- Page speed: Optimize CSS, JavaScript, and images.
- Structured data (Schema Markup): Help Google understand your content.
- 404 pages: Create custom error pages with helpful links.
- Core Web Vitals: Improve metrics like LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift).
Use tools like Google Search Console and PageSpeed Insights for monitoring and improvements.
6. Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these practices as per Google’s SEO Guide:
- Keyword stuffing
- Cloaking or misleading redirects
- Buying backlinks (violates Google’s guidelines)
- Duplicate content without canonical tags
- Neglecting mobile usability
- Slow-loading pages
Always focus on providing value to users rather than trying to “game” the algorithm.
SEO in digital marketing is a long-term strategy that yields significant benefits when done right. By following Google’s SEO Starter Guide and best practices mentioned above, you can ensure your website is optimized not just for rankings, but also for user satisfaction and credibility.
Investing in ethical, content-driven SEO will continue to be a powerful digital marketing strategy as search engines become even smarter.
Best PPC SertviceCompany in India – Drive Results with Irade Technologies
In today’s digital-first landscape, having a strong online presence isn’t just important—it’s essential. With users spending more time online and competition rising in every niche, businesses need an edge to stand out. That’s where PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising comes in. If you’re searching for the best PPC services in India that deliver measurable results, look no further than Irade Technologies—the leading PPC company in India.
At Irade Technologies, we specialize in delivering data-driven, ROI-focused PPC campaigns that generate real business outcomes—whether that means more leads, more sales, or greater brand visibility. With our team of certified experts and tailored strategies, we help brands scale profitably through platforms like Google Ads, Meta (Facebook) Ads, YouTube, Bing, and more.
What is PPC Advertising?
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising services involve paying a fee each time your ad is clicked. Rather than earning visits organically, you’re buying them. From Google Search Ads to Instagram Promotions and Shopping Ads, PPC is one of the fastest ways to bring targeted traffic to your website.
But a successful PPC campaign requires much more than just placing bids. It demands:
Smart targeting
Compelling ad copy
High-converting landing pages
A/B testing
Real-time performance tracking
That’s exactly what Irade Technologies, a leading PPC company in India, delivers.
Why Choose Irade Technologies as Your PPC Partner?
Choosing the right PPC agency can make or break your digital marketing success. As the best PPC management company in India, Irade Technologies builds customized, goal-driven strategies to help clients dominate the digital ad space.
1. Experienced & Certified PPC Specialists
Our team of Google-certified professionals has managed successful campaigns for industries such as e-commerce, healthcare, education, real estate, and SaaS. With years of experience, we know how to make every click count.
2. Full-Funnel PPC Strategy
From brand awareness to conversions, we build PPC funnels that guide your audience every step of the way. Whether you want to drive sales or generate leads, our PPC strategies are tailored to meet your goals.
3. End-to-End Campaign Management
We handle it all—from keyword research, ad creation, and targeting to conversion tracking and performance optimization. Our holistic approach ensures that you maximize ROI on every rupee spent.
4. Transparent and Actionable Reporting
We believe in full transparency. You’ll get in-depth reports that showcase click-through rates (CTR), conversions, cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS)—along with actionable insights for growth.
5. Proven Success Track Record
As one of the top providers of PPC advertising services in India, we have delivered proven ROI improvements for numerous clients. Many of them have seen a 50% reduction in ad spend while doubling their leads.
Our Core PPC Advertising Services in India
We offer a comprehensive range of PPC services in India, designed to drive traffic, leads, and sales across digital platforms.
✅ Search Ads
Appear at the top of Google results for relevant keywords. Perfect for capturing high-intent leads actively searching for your products or services.
✅ Display Ads
Reach over 90% of internet users with engaging visual ads across Google’s Display Network. Ideal for brand building and remarketing.
✅ Google Shopping Ads
Perfect for e-commerce businesses. Showcase your product catalog right on the search results page with price, image, and reviews.
✅ Social Media Ads
Run highly targeted ads on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and YouTube to connect with audiences based on interests, behaviors, and location.
✅ Local Services Ads
Appear at the top of search results when users look for services in your area. Great for local businesses and service providers.
✅ Remarketing Ads
Reconnect with users who’ve already visited your site. These ads are cost-effective and boast some of the highest conversion rates.
Specialized PPC Services We Offer
As a best PPC management company in India, we go beyond basic ads to offer:
Advanced Keyword Research – Identify low-cost, high-converting keywords.
Landing Page Optimization – Improve conversion rates with tailored page design and messaging.
A/B Split Testing – Test different versions of ads and landing pages to boost performance.
Bing & Google Ads Management – Multi-platform campaign management for broader reach.
Comprehensive Campaign Audits – Identify what’s working and what needs improvement.
Our Proven PPC Campaign Process
Our structured approach ensures that every campaign is aligned with your goals and optimized for success:
1. Initial Consultation
We begin by understanding your business objectives, target audience, and competitive landscape.
2. Custom Strategy Development
Based on our research, we craft a personalized strategy including keyword selection, ad creatives, and budget allocation.
3. Campaign Setup
We configure ad groups, target locations, bidding strategies, and conversion tracking to ensure accuracy and reach.
4. Monitoring & Optimization
We continuously monitor key metrics (CTR, CPC, ROAS) and make data-backed optimizations.
5. Transparent Reporting
Receive regular updates on campaign performance along with expert insights and suggestions.
6. Ongoing Campaign Refinement
PPC is never “set it and forget it.” We tweak and scale campaigns for ongoing success.
Industries We Serve
As a leading PPC services provider in India, we support businesses across a wide range of sectors:
E-commerce
Healthcare
Education
Travel & Hospitality
Real Estate
B2B & SaaS
Legal & Finance
Whether you’re a startup or an established brand, we help you grow faster with PPC.
Why PPC Works for Every Business
The beauty of pay-per-click advertising services is its flexibility and scalability. No matter your industry or budget size, PPC works because it delivers:
Instant Visibility
Targeted Reach
Real-time Analytics
Full Budget Control
High ROI Potential
When executed by a skilled team like Irade Technologies, PPC can become one of your most powerful customer acquisition tools.
Get Started with Irade Technologies – The Leading PPC Company in India
If you’re looking for a trusted partner to grow your business with PPC advertising services in India, choose Irade Technologies—a name synonymous with transparency, performance, and results.
📞 Contact Us Today: +91 75308 17898
📧 Email: info@iradetechnologies.com
📍 Location: A‑502, Street No. 16, Gagan Vihar, Bhopura, Ghaziabad – 201005
Let Irade Technologies help you turn clicks into customers with cutting-edge pay-per-click advertising services tailored to your unique needs.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page) to winning within an AI-driven ecosystem
Looking ahead to 2025, the trends we’re seeing now will not just continue—they will accelerate and solidify into the new standard for SEO. The central theme is a dramatic pivot from winning on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page) to winning within an AI-driven ecosystem. The goal is no longer just to be the #1 blue link. It’s to be the definitive, trusted source that powers the entire search experience, from AI summaries to discovery on new platforms.
The Overarching Mega-Trend: The “AI-Mediated” Web
In 2025, we won’t just be “optimizing for search engines”; we’ll be optimizing for an AI layer that sits between the user and the web. Google’s AI Overviews will be the norm, not the exception. This changes everything.
- Impact: Massive potential for “zero-click” or “AI-answered” queries. Traffic for simple informational searches will decline. The value of a click will go up, as users who click through will have more complex needs.
Top 7 SEO Trends for 2025
Here are the top 7 key SEO trends that will define success in 2025.
1. Optimizing for the AI Answer Engine
This is the evolution of classic SEO. Your content’s primary job is to be so clear, authoritative, and well-structured that Google’s AI chooses it as a citable source for its AI Overviews.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: Being featured in an AI Overview is the new “position zero.” It provides immense brand visibility and authority, even if it doesn’t result in a direct click every time.
- What to do:
- Answer Concisely: Structure content with clear headings (H2s, H3s) that ask and directly answer questions.
- Use Advanced Schema: Implement specific structured data like FAQPage, HowTo, and ProfilePage to give AI explicit context about your content and expertise.
- Focus on Data and Statistics: AI loves to pull in specific, citable data points. Publish original research and statistics.
- Become a Named Entity: Build your brand and authors into recognized “entities” in Google’s Knowledge Graph, so the AI knows who you are.
2. The Unassailable Value of E-E-A-T and First-Hand Experience
As AI generates a flood of generic, soulless content, Google’s top priority is to find and reward authentic, human experience. The first “E” in E-E-A-T (Experience) is the new superpower.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: It’s the only real defense against generic AI content. Google’s systems are actively being trained to differentiate between content that rehashes information and content that demonstrates true, first-hand experience.
- What to do:
- Show, Don’t Just Tell: Use original images and videos of you using the product or being at the location.
- Authoritative Bios: Create detailed author pages linking to their social profiles and credentials, proving they are real experts.
- Tell Unique Stories: Infuse content with personal anecdotes, case studies, and real-world learnings that an AI could not replicate.
3. The Great Unbundling: SEO Beyond Google
Relying 100% on Google for discovery is becoming a high-risk strategy. Younger demographics, in particular, use platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and even Reddit as their primary search engines.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: User behavior is fragmenting. People go to TikTok for “how-to” videos, Reddit for authentic reviews, and YouTube for in-depth tutorials. Your brand needs to be discoverable where your audience is searching.
- What to do:
- Treat YouTube as a primary search engine. Optimize video titles, descriptions, and transcripts with keywords.
- Create “Searchable” Short-Form Video: Create TikToks and Reels that directly answer common questions in your niche.
- Engage on Reddit: Monitor and participate in relevant subreddits to build authority and understand what real users are asking.
4. Topical Depth and Strategic Content Pruning
Broad, shallow websites will fail. The future belongs to specialists who own their niche. This means not only creating deep content clusters but also removing content that doesn’t meet E-E-A-T standards.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: Google’s “site-wide” quality signals are stronger than ever. A handful of low-quality, unhelpful articles can drag down the rankings of your entire site.
- What to do:
- Build Content Hubs: Focus on owning a topic from every angle with a pillar page and supporting cluster content.
- Conduct Regular Content Audits: Be ruthless. If an article is outdated, thin, or getting no traffic, either update it significantly or delete it and redirect the URL. Less is often more.

5. Zero-Friction User Experience as a Ranking Factor
If a user does click through from an AI Overview, their patience will be thinner than ever. Your site must be lightning-fast, intuitive, and deliver on its promise instantly.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: Core Web Vitals (CWV) are table stakes. The new focus is on the holistic user journey. A confusing or slow page will lead to an instant “pogo-stick” back to the SERP, telling Google your site was unhelpful.
- What to do:
- Obsess over Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Ensure your page is responsive and interactive immediately.
- Simplify Navigation: Help users find what they need in the fewest clicks possible.
- Remove Intrusive Elements: Aggressive pop-ups and ads will be even more detrimental to rankings.
6. The New ROI: Moving Beyond Clicks and Rankings
Traditional SEO KPIs are becoming outdated. If AI Overviews are answering questions directly, tracking your rank for an informational keyword might be a vanity metric. The C-suite will need to understand a new definition of SEO success.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: The value of SEO will be measured by its overall contribution to business goals, not just organic traffic.
- What to do:
- Track “Answer Engine Optimization” (AEO): Measure how often your brand is cited as a source in AI Overviews.
- Measure Brand Lift: Track the growth of branded search queries (“your brand name” + “topic”). This shows your brand is becoming an authority.
- Focus on Conversions: Tie SEO efforts directly to bottom-of-the-funnel metrics like leads, sign-ups, and sales.
7. Brand as the Ultimate Moat
In a world where the top of the SERP is a blend of AI summaries, ads, and rich snippets, the one thing a user can reliably choose is a brand they trust.
- Why it will dominate in 2025: A strong brand causes users to actively seek you out. They will scroll past AI Overviews and competitors to click on the result from the brand they know and respect.
- What to do:
- Invest in Digital PR: Earn high-authority mentions and links that build brand recognition.
- Build a Community: Use newsletters, social media, and forums to create a loyal following.
- Deliver a Consistent, High-Quality Experience: Every interaction a user has with your brand must reinforce their trust.
In summary, 2025 will reward the authentic, the authoritative, and the agile. The SEO professionals who thrive will be those who stop chasing algorithms and start building brands and content libraries that are so genuinely helpful that both humans and AI recognize them as the best possible answer.
How to Duplicate or Migrate a WordPress Website Using the All-in-One WP Migration Plugin
Migrating a WordPress website can feel like a complex and risky task, especially for those who aren’t developers. Whether you’re moving your website to a new host, changing domains, or creating a clone for staging or development purposes, the process can seem intimidating. Fortunately, there’s an easy and reliable way to handle this — the All-in-One WP Migration plugin.
This powerful WordPress plugin allows users to duplicate or migrate a full WordPress website, including the database, media files, plugins, and themes, with just a few clicks — no coding required. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to successfully duplicate or migrate your WordPress website using the All-in-One WP Migration plugin.
Why Use All-in-One WP Migration?
Before diving into the how-to, let’s look at why All-in-One WP Migration is so widely recommended.
Benefits:
- No technical skills required: Perfect for beginners and non-developers.
- Complete backup and restore: Exports everything — database, media, plugins, and themes.
- Bypasses upload size limits (with premium extension).
- Compatible with most hosts.
- Supports find-and-replace for URLs and paths.
- Cloud storage options (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive).
All-in-One WP Migration has over 5 million active installations and glowing reviews—and for good reason. It simplifies a typically stressful process into less than an hour.
Prerequisites for Migration
Before we begin, here’s what you’ll need:
- Access to the WordPress admin dashboard for both your old (source) and new (destination) site.
- Installed WordPress on the new site.
- The All-in-One WP Migration plugin is installed on both sites.
- Optional: FTP access or cPanel, especially for upload limit increases.
Step 1: Install All-in-One WP Migration on the Source Website
The source site is the website you want to duplicate or move.
- Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard.
- Go to Plugins > Add New.
- Search for “All-in-One WP Migration“.
- Click Install Now, then click Activate.
Once activated, you’ll see a new menu item called All-in-One WP Migration in the sidebar.
Step 2: Export the Website from the Source
- Navigate to All-in-One WP Migration > Export.
- Click on the “Export To” dropdown.
Choose File.
You can also choose other destinations such as:
- FTP
- Dropbox
- Google Drive
- OneDrive (with premium extensions
- Wait as the plugin compiles your website into a single
.wpressfile. - When the export is finished, click Download to save the file to your computer.
Optional: You can exclude files or replace URLs during this process if you’re changing domains or want to reduce file size.
Step 3: Prepare the New (Destination) Website
This is where you will import your duplicated website.
- Install a fresh version of WordPress on your new host or domain.
- Log in to the admin dashboard.
- Install the All-in-One WP Migration plugin the same way as on the source site:
a. Go to Plugins > Add New
b. Search and install All-in-One WP Migration
c. Click Activate
Step 4: Import the Website to the Destination Site
- Go to All-in-One WP Migration > Import.
- Click the Import From dropdown, and choose File.
- Select the
.wpressfile you downloaded earlier. - The plugin will upload and extract the file. This may take a while, depending on file size and server speed.
If your file is larger than the default 512MB limit:
- You can buy the Unlimited Extension from ServMask.
- Or increase the upload size limit by editing:
a..htaccess
b.php.ini
c.wp-config.php
We’ll explain how to do this below.
- Once uploaded, you’ll see a warning saying “This action will overwrite your website…” — click Proceed.
- Let the tool complete the process (it will update the database, media, plugins, and themes).
Step 5: Log In to the New Website
Once the import is finished, the system logs you out.
- Use the original admin credentials from the source website to log in.
- If you forget them, you can use
phpMyAdminto reset the admin password or contact your host.
Step 6: Final Cleanup and Post-Migration Steps
After migration, you need to finalize your setup:
1. Reset Permalinks
- Go to Settings > Permalinks
- Click Save Changes (no need to modify anything)
- This regenerates the
.htaccessfile for correct URL routing
2. Test Everything
- Browse your site to ensure images load, links work, and the design is intact.
- Check contact forms, login pages, and any dynamic content.
- Verify that plugins are functioning properly.
3. Update Site URL (If Domain Has Changed)
If you’re changing the domain:
- Use a plugin like Better Search Replace to update old URLs in the database.
- Alternatively, use the find/replace feature during export or import in All-in-One WP Migration.
How to Increase the Upload Limit (Optional)
If your export file is larger than the allowed size, you have a few options:
Option 1: Edit .htaccess
php_value upload_max_filesize 512M
php_value post_max_size 512M
php_value memory_limit 512M
php_value max_execution_time 300
php_value max_input_time 300
Option 2: Edit php.ini
upload_max_filesize = 512M
post_max_size = 512M
memory_limit = 512M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
Option 3: Edit wp-config.php
Add this before the /* That's all, stop editing! */ line:
@ini_set('upload_max_size', '512M');
@ini_set('post_max_size', '512M');
@ini_set('memory_limit', '512M');
If these options don’t work, contact your hosting provider or use the plugin’s Unlimited Extension.
Use Cases for Duplicating or Migrating Your WordPress Site
- Changing Hosting Providers
- Switching Domains
- Moving from a Localhost to Live Server
- Creating a Staging Environment
- Backing up a Site Before Redesign
- Duplicating a Template for Reuse
All-in-One WP Migration is flexible enough to handle all of these scenarios without needing technical know-how.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Import fails or hangs | Increase PHP limits (memory, timeout) or use the Unlimited extension |
| Site broken after import | Reset permalinks, clear cache, disable conflicting plugins |
| Incorrect URLs or broken links | Use “Better Search Replace” to update old URLs in the database |
| Login fails after migration | Use old credentials or reset password via phpMyAdmin |
Conclusion
Duplicating or migrating a WordPress website doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the All-in-One WP Migration plugin, the process becomes simple, fast, and safe. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, this tool streamlines everything — from backups to full site transfers — without the need for FTP, MySQL, or code.
Just follow the steps in this guide:
- Install the plugin on both sites
- Export from the old site
- Import to the new site
- Finalize and test
In just a few clicks, you’ll have a fully functional duplicate of your site — ready to go live, test, or develop further
Google’s March 2025 Core Update: Impact and SEO Strategies
Google’s algorithm updates are critical for businesses and website owners aiming to maintain or improve their rankings on search engine result pages (SERPs). On March 13, 2025, Google released its latest core update, marking another significant shift in how content is ranked. With the rollout expected to take up to two weeks, SEO professionals and content creators need to understand the implications of this update and how to adjust their strategies accordingly.
What is a Google Core Update?
Google regularly updates its search algorithms to improve the relevance and quality of search results. A core update is a broad change that affects search rankings across various industries. Unlike minor tweaks, core updates can significantly alter website visibility, favoring sites with high-quality content and user-focused optimizations.
According to Google’s official documentation, these updates are designed to ensure that searchers receive the most relevant and authoritative information available. While Google does not reveal the exact algorithmic changes, past updates have focused on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness), page quality, and content relevance.
Key Changes in the March 2025 Core Update
Although Google has not disclosed specific ranking factors, SEO experts have identified key trends from early data analysis. Below are some of the primary changes observed:
1. Greater Emphasis on E-E-A-T
Google continues to refine its emphasis on Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Websites demonstrating real-world expertise and high authority in their niche are more likely to rank higher. This means that:
- Medical, financial, and legal websites (YMYL – Your Money, Your Life) are being scrutinized more rigorously.
- Author bylines, credentials, and expert contributions are playing a more significant role.
- Citations and backlinks from reputable sources are weighted more heavily.
2. Quality Content Over Quantity
Google has increasingly favored depth and originality over high content volume. Sites that frequently produce low-value or AI-generated content without human oversight may experience ranking drops.
To ensure compliance:
- Create long-form, well-researched content that adds real value.
- Avoid keyword stuffing and prioritize natural language processing (NLP).
- Use structured data to enhance the clarity of your content for search engines.
3. User Experience (UX) & Core Web Vitals
Page experience continues to be a critical ranking factor. Google’s Core Web Vitals update in 2021 emphasized metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). The March 2025 update expands on this by prioritizing:
- Faster page speeds and optimized mobile responsiveness.
- Reduction in intrusive interstitials (pop-ups) that disrupt user experience.
- Improved accessibility features, including alt text for images and clear site navigation.
4. AI-Generated Content & Google’s Stance
With the rise of AI content generators, Google has tightened its stance on AI-driven content. AI-generated articles that lack original insights or human editorial oversight may be devalued. However, AI-assisted content that is fact-checked and well-structured can still perform well.
Who Will Benefit from This Update?
Certain industries and content strategies seem to have gained a boost from the March 2025 core update:
- Expert-driven blogs and websites with in-depth research and case studies.
- Authoritative news portals that provide fact-checked, timely information.
- E-commerce websites with well-optimized product descriptions and unique content.
- Local businesses with strong user engagement metrics and high-quality customer reviews.
Who Might Be Negatively Impacted?
On the flip side, some websites have experienced ranking drops:
- Thin affiliate sites that provide minimal value beyond outbound links.
- Low-quality AI-generated content mills that lack editorial oversight.
- Websites with slow-loading pages and poor mobile usability.
- Sites with outdated or misleading content that lack trustworthiness.
SEO Strategies to Adapt to the March 2025 Core Update
If your website has been negatively affected by this update, here are some actionable steps to recover and improve your rankings:
1. Audit and Improve Content Quality
- Conduct a content audit to identify outdated or low-performing pages.
- Refresh old articles with new data, insights, and multimedia elements.
- Enhance your E-E-A-T signals by including expert quotes, references, and verifiable information.
2. Optimize Technical SEO
- Improve page load speed by optimizing images, using a CDN, and minifying CSS/JavaScript.
- Ensure that your site is fully mobile-friendly and passes Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Fix broken links, duplicate content, and schema markup errors.
3. Leverage Structured Data & Schema Markup
Google rewards websites that use structured data to provide better context. Implement:
- FAQ schema for informative content.
- Product schema for e-commerce listings.
- Author schema to highlight expert contributors.
4. Enhance User Experience (UX)
- Reduce intrusive pop-ups and ads that interfere with navigation.
- Optimize site structure for better internal linking and ease of access.
- Improve engagement signals like dwell time, bounce rate, and click-through rates (CTR).
5. Monitor Performance with Google Search Console
- Use Search Console to track ranking changes, indexing issues, and crawl errors.
- Check the Page Experience report to identify and fix UX problems.
- Regularly monitor Google Analytics for traffic trends and user behavior shifts.
Final Thoughts
Google’s March 2025 Core Update is another step toward higher-quality search results that benefit users. The key to thriving in this evolving SEO landscape is to prioritize content quality, technical optimization, and user experience. Websites that consistently provide value, maintain credibility, and adapt to these changes will continue to perform well in search rankings.
Cleaning Services Digital Marketing Agency in USA
Irade Technologies is a leading digital marketing agency promoting cleaning businesses in the USA. Whether you’re offering house cleaning, carpet cleaning, gutter cleaning, mold removal, or commercial cleaning services, our tailored marketing strategies ensure you reach the right audience effectively.
This article explores how Irade Technologies helps cleaning service businesses grow through search engine optimization (SEO), social media optimization (SMO), Google My Business (GMB) SEO services, and customized SEO packages for small businesses. Irade Technologies offers the best digital marketing solutions for cleaning businesses in the USA. Whether you need local SEO, social media management, PPC advertising, or reputation management, our expert team ensures your cleaning services rank at the top.

1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for Cleaning Services
SEO is the backbone of digital marketing, ensuring your cleaning business ranks high in search engine results for relevant keywords. Irade Technologies offers:
- On-Page SEO – Optimizing website content, meta descriptions, and headers with targeted keywords like “carpet cleaning near me,” “house cleaning services near me,” and “pressure washing near me.”
- Off-Page SEO – Building high-quality backlinks and local citations to improve domain authority.
- Technical SEO – Enhancing website speed, mobile responsiveness, and structured data for better search rankings.
- Local SEO – Optimizing for Google My Business to appear in local searches like “roof cleaning near me” and “office cleaning services near me.”
2. Google My Business (GMB) SEO Services
A well-optimized Google My Business profile is crucial for local cleaning businesses. Irade Technologies helps you:
- Set up and verify your GMB listing
- Optimize your business profile with relevant keywords
- Manage customer reviews and ratings
- Post regular updates and offers
- Ensure accurate location and contact details
3. Social Media Optimization (SMO) for Cleaning Services
Social media is a powerful tool to engage potential clients. We offer:
- Content creation for Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn
- Engaging visuals and videos showcasing cleaning services
- Targeted ads for specific locations
- Regular interaction and community building
4. Customized SEO Packages for Small Businesses
We understand that small cleaning businesses need affordable marketing solutions. Our low-cost SEO services include:
- Keyword research for niche services like “attic cleaning” and “trash can cleaning service”
- Website audit and optimization
- Local citation building
- Content marketing strategies
- Affordable backlinking solutions
5. PPC Advertising for Cleaning Services
Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns help businesses gain immediate visibility. We create targeted Google Ads and social media ads for services such as:
- Residential cleaning services
- Janitorial services
- Industrial cleaning services
- Post-construction cleaning
- Fire damage clean-up
6. Content Marketing for Cleaning Companies
Quality content helps build brand authority and attract organic traffic. We provide:
- Blog writing on topics like “how to find the best cleaners near me”
- Informative guides on mold removal, vent cleaning, and more
- Customer testimonials and case studies
- Email marketing campaigns
7. Website Design and Development for Cleaning Businesses
A professional website is crucial for credibility. Our web design services include:
- Mobile-friendly and SEO-optimized websites
- Booking and scheduling integration
- Fast-loading pages
- Secure payment gateways for service bookings
8. Reputation Management for Cleaning Companies
Online reputation influences customer decisions. We help with:
- Managing and responding to reviews
- Encouraging satisfied customers to leave feedback
- Handling negative reviews professionally
- Building trust through social proof
9. Video Marketing for Cleaning Services
Videos increase engagement and trust. Our services include:
- Promotional videos showcasing cleaning services
- Customer testimonial videos
- Before-and-after cleaning videos
10. Analytics and Performance Tracking
We provide in-depth analytics to measure success:
- Monthly SEO reports
- Google Analytics tracking
- Conversion rate optimization
- Performance metrics for PPC and social media
Boutiques Services Digital Marketing Agency in USA
Irade Technologies, a leading digital marketing company, specializes in providing top-notch marketing solutions for online boutiques in the USA. Whether you’re selling plus-size clothing online, luxury fashion, boutique blouses, or designer jewellery, our services help you enhance visibility, increase conversions, and grow your brand.
With Irade Technologies, online boutiques in the USA can take their businesses to the next level through strategic digital marketing. Our comprehensive services, including SEO, SMO, Google My Business optimization, and affordable SEO packages, ensure that your boutique attracts the right audience and achieves sustainable growth. Contact us today to transform your online fashion boutique into a thriving brand!
Why Digital Marketing is Essential for Online Boutiques
With the rise of eCommerce, consumer behavior has shifted towards online shopping, making digital marketing an essential strategy for fashion retailers. Here’s why:
- Increased Online Presence: A strong digital footprint helps your boutique gain visibility among potential customers.
- Brand Authority: Strategic content marketing, social media presence, and SEO enhance brand reputation.
- Higher Sales & Conversions: Targeted advertising and conversion optimization ensure higher revenue.
- Competitive Edge: Outrank competitors with expert SEO and paid marketing campaigns.
IraDe Technologies’ Digital Marketing Services for Online Boutiques
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for Online Boutiques
SEO plays a critical role in improving the organic visibility of your online store. We provide:
- Keyword Optimization: Targeted keywords like “plus size women’s clothing online” and “luxury brand online shop.”
- On-Page SEO: Optimizing product pages, meta tags, descriptions, and images.
- Technical SEO: Enhancing website speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data.
- Content Marketing: Blog writing and guest posting to boost domain authority.
- Local SEO: Google My Business SEO services to increase local store rankings.
Social Media Optimization (SMO) Services
Social media is a powerful tool for brand promotion. Our SMO services include:
- Content Creation: High-quality images, videos, reels, and engaging captions.
- Platform Optimization: Managing Instagram, Facebook, Pinterest, and TikTok pages.
- Influencer Marketing: Partnering with fashion influencers for brand endorsements.
- Paid Ads Management: Running social media ad campaigns to target the right audience.
Google My Business (GMB) SEO Services
For boutiques with physical stores or a local target audience, we optimize GMB listings by:
- Adding high-quality images & descriptions
- Optimizing business categories & services
- Encouraging customer reviews & responding to feedback
- Implementing local SEO strategies to rank higher in Google Maps searches
SEO Packages for Small Businesses
We offer cost-effective SEO packages tailored for small boutique owners. These include:
- Basic SEO: Essential on-page SEO and keyword optimization.
- Advanced SEO: Competitor analysis, backlinking, and content marketing.
- E-commerce SEO: Focused on product pages, category pages, and conversion rate optimization.
Low-Cost SEO Services for Budget-Conscious Brands
Startups and small boutiques benefit from our affordable SEO services, which include:
- Optimized product descriptions
- Technical SEO improvements
- Basic link-building strategies
- Social media SEO integration
Industry-Specific Digital Marketing Strategies
For Plus-Size Clothing Online Stores
- Keyword Targeting: “Plus size clothing online” and “plus size women’s clothing online.”
- Influencer Collaborations: Partnering with plus-size fashion influencers.
- Content Marketing: Blogs on body positivity and styling tips.
- Visual Storytelling: High-quality images and videos featuring real customers.
For Online Jewelry Boutiques
- SEO for Jewelry Stores: Targeting keywords like “online jewelry boutique.”
- Instagram & Pinterest Marketing: Leveraging visual platforms for engagement.
- Luxury Branding: Creating a premium image through high-quality content and influencer tie-ups.
For Women’s Boutique Blouses and Clothing Stores
- Style Guides & Fashion Tips: Engaging blog content to attract fashion-conscious buyers.
- Email Marketing: Personalized campaigns for customer retention.
- Facebook & Google Shopping Ads: Paid promotions targeting women shoppers.
Robots Refresher: Power and Functionality of Robots.txt
In the world of web development and internet crawling, the robots.txt file is an unsung hero that helps manage how automated bots interact with a website. If you’ve ever wondered how search engines or web crawlers know which pages to index or skip, or how website owners control that access, the answer lies in the humble robots.txt file. This article will delve into the history, importance, and usage of robots.txt, giving you an in-depth understanding of why it’s such a vital tool for both website owners and web crawlers.
What is Robots.txt?
At its core, robots.txt is a plain text file stored on a website’s server that provides instructions to web crawlers (also called spiders or bots). These bots are automated programs that browse the internet to index web pages for search engines, collect data, or perform other tasks. The robots.txt file tells these bots which areas of a website they are allowed to access, and which they should avoid. Essentially, it serves as a gatekeeper, allowing website administrators to control the traffic of web crawlers.
Most websites have a robots.txt file, and it’s usually located at the root of the website. For example, if you wanted to view a site’s robots.txt file, you would simply add /robots.txt to the end of the site’s URL. So, for Google’s robots.txt file, the address would be developers.google.com/robots.txt.
How Does Robots.txt Work?
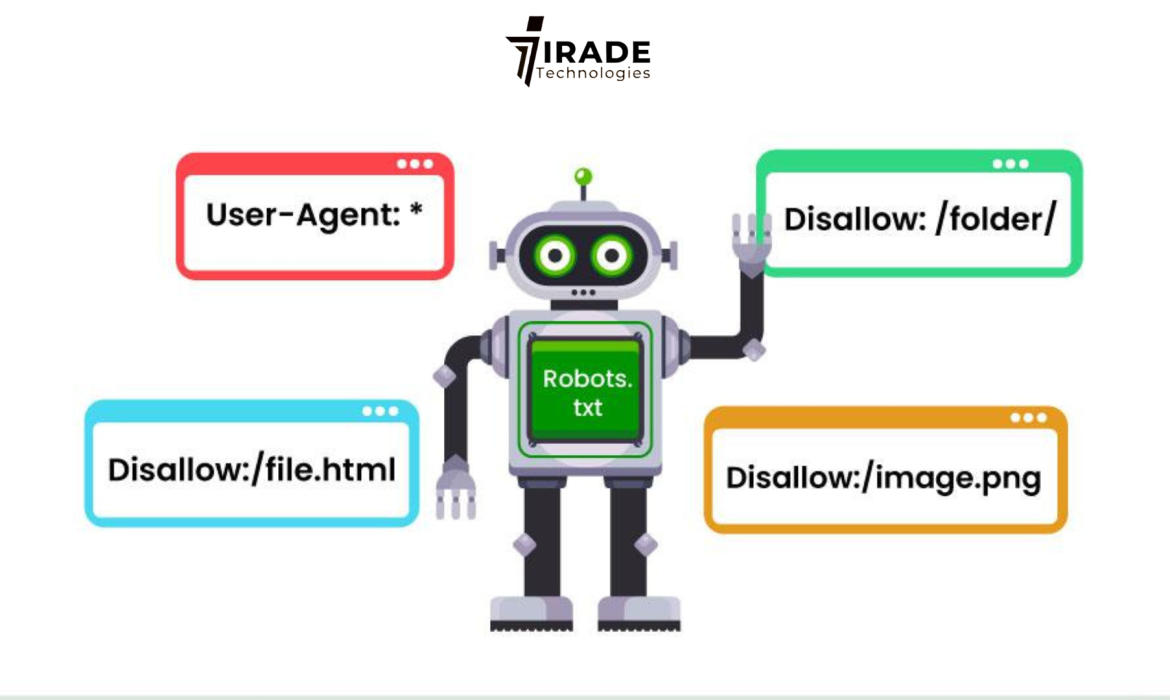
A robots.txt file operates on a simple premise: it consists of directives that tell web crawlers what they are permitted to crawl and what they should refrain from crawling. This control is achieved through two primary directives: User-agent and Disallow.
User-agent: This refers to a specific crawler or bot. Each bot identifies itself with a user-agent string. For example, Googlebot is Google’s search engine crawler, while Bingbot is Bing’s. This allows website owners to target specific bots with their instructions. If a site owner wants to give different rules for different crawlers, they can do so using separate “User-agent” entries.
Disallow: This directive tells the bot not to crawl a particular directory or page. For example, if you don’t want a bot to crawl your “admin” section, the robots.txt file could include a line like:
Disallow: /admin/
The combination of these two elements gives website owners a great deal of control over which content is available for automated crawling. For instance, a website might want to block certain pages (such as login or registration pages) from being crawled to avoid unnecessary strain on the server or to prevent the indexing of sensitive information.
While robots.txt can control a crawler’s access to a site, it’s important to note that it doesn’t provide any security measures. It’s simply a guideline for well-behaved bots. Malicious crawlers or those that disregard the rules can still access restricted content if they wish. However, most commercial bots, like Googlebot, will respect the instructions given in robots.txt files.
Why Do Websites Use Robots.txt?
There are several reasons why website owners choose to implement robots.txt files, ranging from optimizing crawling efficiency to improving server performance. Here are some key benefits:
Crawling Efficiency: Websites can have hundreds or even thousands of pages. Automatically crawling all of them may not be necessary or efficient, especially for large, dynamic sites. Robots.txt allows site owners to direct crawlers to relevant pages, improving the overall efficiency of the indexing process.
Avoiding Overloading Servers: Some websites generate pages dynamically, meaning they can create a significant load on servers if crawlers attempt to access every URL. By using robots.txt, administrators can prevent these pages from being crawled, ensuring that the servers aren’t unnecessarily burdened.
Preventing Indexing of Sensitive Content: Websites that contain private or sensitive information, such as login pages or administrative tools, may want to prevent these from appearing in search engine results. By adding “Disallow” rules for these areas, the robots.txt file helps keep them hidden from search engines.
Facilitating Focused Crawling: A website might want crawlers to focus on particular sections of the site that are most important for SEO purposes. For example, a website selling products may want its product pages crawled and indexed, but it might not want its “thank you” or “checkout” pages to be indexed. Robots.txt provides a simple way to enforce this.
The History and Evolution of Robots.txt
The concept of the robots.txt file dates back to the early days of the web. HTML, the language that powers web pages, was invented in 1991, and web browsers arrived shortly after. By 1994, the first robots.txt file was introduced, allowing webmasters to have some control over which bots could crawl their sites.
This early implementation of robots.txt predates even Google, which wasn’t founded until 1998. The format of the robots.txt file has remained largely unchanged since its inception, which speaks to its simplicity and effectiveness. Even today, a robots.txt file created in the early days of the internet would still be valid and function as intended.
Over time, the robots.txt format has become standardized and even evolved. For example, in 2007, search engines introduced the “sitemap” directive, which allowed webmasters to include a link to an XML sitemap within the robots.txt file. This development helped bots find and crawl the most important pages of a website more effectively.
In 2022, after years of global collaboration, robots.txt became an official IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) proposed standard, solidifying its role in internet infrastructure.
The Flexibility of Robots.txt
One of the great advantages of robots.txt is its flexibility. It is a simple yet powerful tool that allows website owners to exercise granular control over their site’s content. Whether it’s blocking specific crawlers, directing bots to focus on certain areas, or preventing the indexing of certain pages, robots.txt can handle it all.
The format itself is also adaptable. New directives or modifications can be introduced over time to address the evolving needs of the internet. As new types of crawlers, such as those used for artificial intelligence, emerge, robots.txt will likely continue to grow and evolve to accommodate these changes.
Why Robots.txt is Here to Stay
Despite the availability of new technologies and tools, robots.txt is still a cornerstone of the web’s ecosystem. It’s simple, human-readable, and effective, with an established standard that has stood the test of time. While newer formats may emerge, it will likely remain a vital tool for years to come.
The global community’s continued engagement with robots.txt ensures that it remains relevant and effective. There are thousands of tools, software libraries, and communities dedicated to helping developers manage and understand robots.txt files. However, one of the beautiful aspects of robots.txt is its simplicity—it’s easy to edit and read, even without specialized tools.
Conclusion
In a world where web crawlers constantly scan the internet for information, the robots.txt file offers a simple but powerful solution for controlling and managing crawler access. By using it, website owners can optimize their site’s performance, avoid unnecessary server strain, and ensure that sensitive content remains hidden from search engines. With its long history, flexible format, and active community, robots.txt is an essential tool that’s here to stay.
For those eager to learn more about the inner workings of robots.txt and how to fine-tune their web crawlers, the ongoing Robots Refresher series will continue to provide valuable insights. Stay tuned for future installments that will dive deeper into advanced use cases, best practices, and the latest trends in the world of web crawling.
Bakeries Services Digital Marketing Agency in USA
Irade Technologies is a leading digital marketing company and agency that provides tailored solutions specifically for bakeries across the USA. This article will explore the best digital marketing services that can help bakeries like yours stand out from the competition.
When it comes to digital marketing for bakeries in the USA, Irade Technologies offers a comprehensive, affordable, and tailored approach that ensures your bakery stands out. Whether you’re a small local bakery or a larger bakery chain, Irade Technologies has the expertise to help you grow your business online and attract more customers. With our focus on local SEO, social media optimization, and affordable SEO packages, we can help your bakery thrive in today’s competitive digital landscape.
Best Digital Marketing Services for Bakeries
1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for Bakeries
SEO is the foundation of any successful online marketing strategy, and it’s particularly important for bakeries because customers are increasingly turning to search engines to find nearby places to satisfy their cravings. By optimizing your bakery’s website for search engines, you can ensure that your bakery is visible to potential customers when they search for keywords like “best bakery near me,” “Italian bakery near me,” or “fresh bread bakery near me.”
Key Strategies:
- On-page SEO: Optimizing your website’s content, images, and structure to make it search-engine friendly.
- Local SEO: For bakeries with physical locations, local SEO ensures that your bakery shows up when people search for terms like “pastry shop near me” or “cake shop near me.”
- Keyword Research: Identifying high-traffic keywords related to your bakery’s niche, such as “vegan bakery near me,” “sugar-free bakery near me,” or “croissants near me.”
- Content Creation: Creating blogs, recipes, or bakery-related tips that incorporate these keywords, attracting more customers and increasing engagement.
2. Google My Business (GMB) Optimization
For bakeries, having a well-optimized Google My Business (GMB) profile is essential for local search visibility. A properly set up GMB profile enables your bakery to appear in local search results and Google Maps when people search for nearby bakeries. With GMB, potential customers can find your hours of operation, reviews, menu offerings, and even photos of your bakery’s delicious treats.
Key Strategies:
- Complete Your Profile: Ensure that your bakery’s address, phone number, and website URL are accurate and up-to-date.
- Engage with Reviews: Encourage customers to leave positive reviews, and respond to them promptly.
- Upload High-Quality Photos: Showcase your signature pastries, cakes, or artisan breads.
- Update Posts Regularly: Share special promotions, events, or new products directly on your GMB profile.
3. Social Media Optimization (SMO) for Bakeries
Social media is a powerful tool for bakeries to engage with their customers, share tempting photos of their baked goods, and build brand loyalty. Irade Technologies excels in Social Media Optimization (SMO), helping bakeries create a solid presence across platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Pinterest, and TikTok.
Key Strategies:
- Content Creation: Regularly post visually appealing content, such as behind-the-scenes bakery shots, videos of cake decorating, or seasonal pastries.
- Community Engagement: Respond to customer comments, messages, and reviews, showing that your bakery values its customers.
- Targeted Advertising: Use social media ads to target specific demographics, such as people searching for “vegan bakery near me” or “cake box near me.”
4. Email Marketing for Bakeries
Email marketing allows bakeries to nurture relationships with customers and keep them informed about new offerings, special discounts, and seasonal treats. Irade Technologies designs personalized email campaigns that increase customer engagement and drive sales.
Key Strategies:
- Segment Your Audience: Group customers based on their preferences, such as those who prefer Italian bread, croissants, or cupcakes, and send tailored emails.
- Special Offers & Discounts: Send out exclusive discounts, seasonal offers, or loyalty rewards.
- Event Promotion: If your bakery is hosting an event, email marketing can help spread the word and boost attendance.
5. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising for Bakeries
PPC advertising is a fast way to gain visibility and attract new customers to your bakery. By bidding on specific keywords related to your business, such as “best bakery near me” or “Magnolia bakery cakes,” Irade Technologies can help your bakery appear in the paid search results on platforms like Google and Bing.
Key Strategies:
- Targeted Ads: Create ads that target specific bakery-related keywords and local areas.
- Conversion Tracking: Monitor the performance of your ads and adjust them for better results.
- Retargeting Ads: Show ads to customers who have previously visited your bakery website, encouraging them to return.
6. Website Design & Development for Bakeries
A visually appealing and functional website is key to attracting and retaining customers. Irade Technologies helps bakeries design and develop responsive websites that are mobile-friendly, easy to navigate, and optimized for search engines.
Key Strategies:
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure that your bakery website is fully optimized for mobile devices, as many customers will be searching for bakeries on their phones.
- Online Ordering & Delivery: If your bakery offers online ordering, ensure the process is simple and secure.
- Easy Navigation: Ensure that customers can easily find key information like your bakery’s menu, hours, and location.
7. SEO Packages for Small Businesses
Irade Technologies offers customized SEO packages tailored specifically for small bakeries. These packages include everything from keyword optimization and link building to content creation and local SEO strategies. These packages are designed to be affordable for smaller businesses while still providing powerful results.
Key Features:
- Affordable Pricing: Get quality SEO services without breaking the bank.
- Comprehensive Reports: Receive regular updates on your bakery’s SEO performance and rankings.
- Ongoing Support: Continuous monitoring and optimization to ensure your bakery stays ahead of the competition.
8. Low-Cost SEO Services
Many small bakeries are hesitant to invest heavily in digital marketing, especially if they’re just starting out. Irade Technologies offers low-cost SEO services that provide great value for bakeries looking to enhance their online presence without a large budget.
Key Features:
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Affordable SEO services that don’t compromise on quality.
- Customized Approach: Tailored SEO strategies that align with your bakery’s unique needs and goals.
- Local SEO Focus: Special emphasis on local SEO to help bakeries rank higher for location-based searches.
Targeting Specific Bakery Niches
There are many different types of bakeries, and each one has its own unique customer base. Whether you run a vegan bakery, an Italian bakery, a French bakery, or a cake shop, Irade Technologies can create digital marketing campaigns that resonate with your specific audience.
1. Vegan Bakery Marketing
Vegan bakeries are growing in popularity as more customers seek plant-based options. Irade Technologies can help you target vegan customers through keyword optimization, social media, and email campaigns.
2. Wholesale Bakery Marketing
If you run a wholesale bakery, you need to focus on reaching local restaurants, cafes, and retailers who can become long-term clients. Irade Technologies can help you target B2B customers through LinkedIn advertising, content marketing, and local SEO.
3. Italian Bakery Marketing
For Italian bakeries, your marketing should highlight the authenticity and quality of your Italian pastries and bread. Irade Technologies can help you create content that celebrates your bakery’s heritage and connect with customers who love Italian cuisine.
4. Cake Shop Marketing
Cake shops, especially those offering custom cakes for special events, require highly visual marketing. Irade Technologies can create stunning social media campaigns showcasing your cake designs and promoting seasonal or holiday specials.